Table of Contents
The cryptocurrency Bitcoin has been the focus of general interest for some time and with it, the blockchain technology makes this concept possible in the first place. But exactly, what is blockchain technology, and is the hype about the technology justified?
Definition: What is blockchain technology?
The term blockchain comes from English and means blockchain. The “blocks” stand for individual data records that are saved one after the other, creating a kind of data record chain.
In principle, the blockchain is nothing more than a large database that starts with an original block to which new data blocks are always appended chronologically after they have been checked and confirmed. It thus depicts a history of data records (e.g. financial transactions).
What is special about the blockchain database is that it is a distributed database. This means that everyone who participates in the blockchain system saves a complete copy of the data history on their computer. This procedure significantly increases protection against manipulation, since even if a copy is manipulated, there are still many correct copies and the manipulated data record can simply be “sorted out”. In addition, the order of the blocks is additionally secured by a checksum. This prevents the order of the blocks from being changed later.
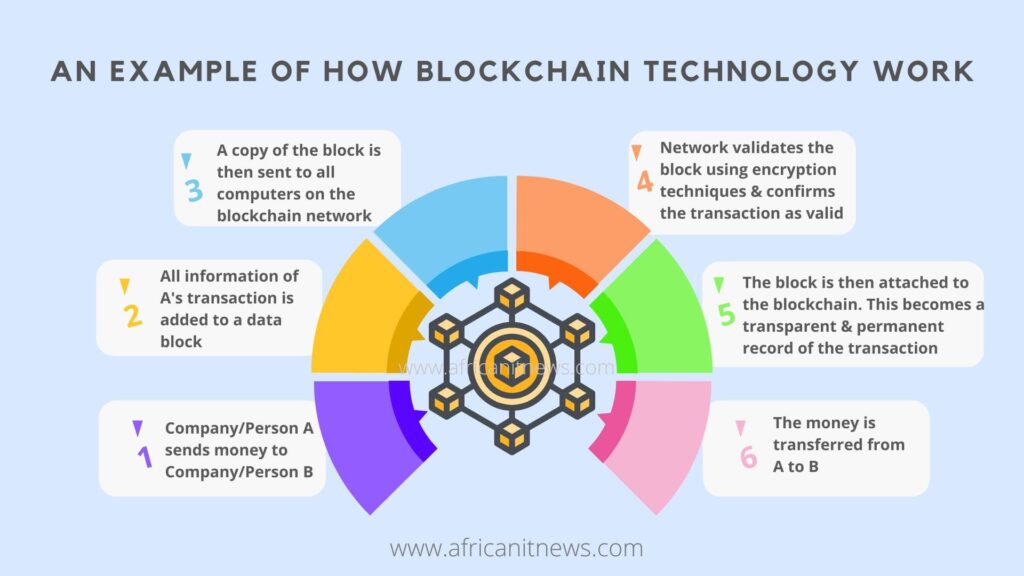
While blockchain is widely used for financial transactions, it is important to understand that it is not limited to one type of information. It can also be used for bookkeeping or for backing up music, photos, or texts.
What can blockchain technology be used for?
After the theoretical basics, two practical application scenarios of the technology will now be explained.
Cryptocurrencies
As already mentioned in the introduction, the most well-known application examples of this technology are cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Cryptocurrencies are a digital form of currency that is traded and exchanged just like regular paper currency. However, unlike paper currencies, cryptocurrencies are not controlled by financial institutions or the government. You should also be aware that not all cryptocurrencies are the same. Each has its unique characteristics and uses.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts (“intelligent contracts”) are contracts based on blockchain technology and do not require a third party (e.g. a notary) to ensure legal certainty. In addition, smart contracts can come into force automatically under certain conditions.
A practical application example of this method is software licensing. Smart contracts make it much easier for the user to purchase licenses. But the license seller also has advantages through the use of Smart Contracts. This makes it possible, for example, for customers to automatically deactivate access to the licensed software if they miss payments.
What are the advantages of blockchain technology?
After two possible practical applications have been explained, the advantages of the technology should now be discussed. So the question is: What added value can it actually provide?
Security
- Once the information has been added to the “blockchain” and verified, it is (in principle) no longer possible to change it
- The complete file is available as a copy on each end device connected to the network.
- Manipulation could be uncovered by comparing the manipulated file with the other files distributed in the network. The result would be an exclusion of the manipulated file, which protects the original data set. This mechanism represents a safeguard against corruption.
Transparency
It is possible to track and check extensions to the blockchain.
Cost savings
Blockchain data can be trusted without trusting the other party. This eliminates the need for third parties who are normally involved as control bodies. This lowers the costs incurred.
Time-saving
The technology works like central and digital bookkeeping and thus reduces the communication effort between the parties involved. In addition, the potential for errors is minimized by automation. This saves time.
Disadvantages of the blockchain – is the hype justified?
A major disadvantage of this technology is the high storage overhead. The blockchain grows with each additional block and the growing amount of data is also stored on every node of the network. As a result, not all transaction scenarios can be mapped in this way. The performance is also a disadvantage because both the verification of the transactions and the synchronization take time. Furthermore, integrating the blockchain into the existing IT architecture is not easy and entails a high level of change management effort.
It is also important that the blockchain is not 100% tamper-proof. If a participant can control more than half of the nodes, manipulation would be possible. Now that the downsides of the technology have been discussed, you might be wondering:
Is the hype justified at all?
A study by the Hasso Plattner Institute for Digital Engineering in 2018 dealt with this topic. The study says that many of the expectations of technology are too high. Overall, it would still be in its infancy. Nevertheless, the researchers see a wide range of potential if the weak points are repaired in the future. This could ensure that the technology can be used in different fields and industries. The future success of the blockchain, therefore, depends on the further development of the technology.
Blockchain as opposed to the cloud?
As a managed service provider, it is our goal to relate new technologies to our work. An interesting perspective in this context is to see blockchain as the antithesis of cloud technology. Because in contrast to the cloud, the data in the blockchain is not stored centrally, but the data storage takes place decentrally on all computers in the network.
In addition, the areas of application of the two technologies are different. While blockchain primarily works in a transaction-related manner and security and traceability are paramount, cloud technology offers a wider range of application areas and is used, among other things, to be able to partially or completely dispense with on-premises hardware.
However, as blockchain technology is still in its infancy and is not limited to financial transactions, it remains to be seen whether its scope will expand further and perhaps see more overlap with cloud technologies in the future.




2 comments
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.